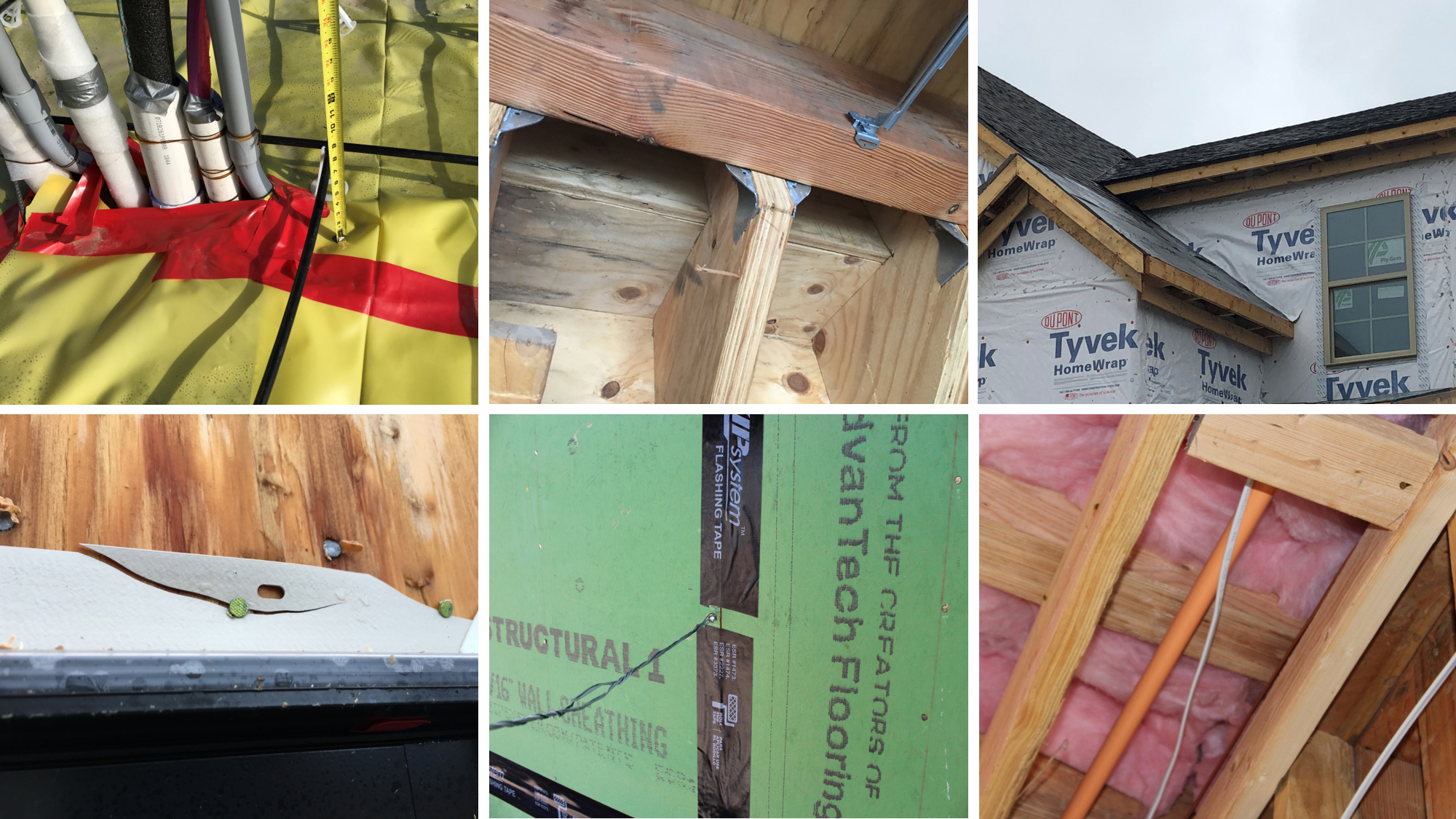
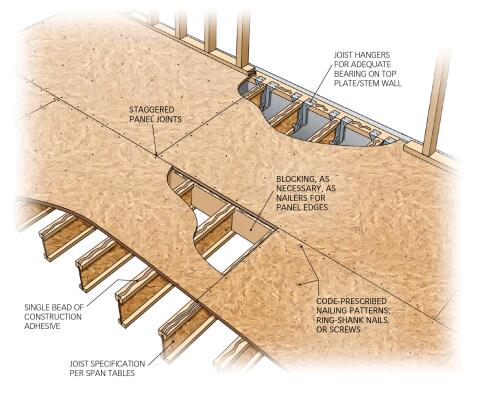
Best Practices For Building Low Deflection Firm Second Floor

Note it gives the allowable deflection based on a fractional span quantity so a larger denominator will yield less deflection.
Best practices for building low deflection firm second floor. Builders design for deflection only typically by holding deflection due to live load to a maximum of l 360 where l is the floor joist span or perhaps a more restrictive l 480. For any structural member deflection limits must be satisfied based on the building code. For example for a 30 foot span l deflection of up to 1 5 inches in a single floor member would be permissible. Building framing systems.
For new home builders a squeaky or bouncy floor is a sign of substandard or code minimum construction practices the effect of which can erode their reputation for delivering comfortable quality. Some experts say the deflection should be no more than l 360 for floor spans up to 15 ft. For example a floor joist spanning 20ft 240 inches a deflection limit of 2 3inch for live loads and 1inch for total loads. In any case most designs limit the actual deflection to v2 in.
For example the maximum deflection for a joist span of 15 is 15 12 360 1 2. Of course many rooms are more than 12 feet across so joist manufacturers tables tell you the maximum span lengths under certain circumstances. This is the second of two articles on proper floor framing. Divide the total span of the floor joists in inches by 360 to determine the maximum amount the floor can give in the middle under a live load of 40 lb sq.
In canada the building code includes limits on floor vibration. That upgrade prescribes a 0 3 inch deflection across a 12 foot span. He importance of properly designed foundations was discussed in chapter 6 coastal foundations and best practices. For even less deflection look for span tables that chart an l 480 floor deflection ratio.
It s tough to field test for deflection but you may be able to find the design deflection on the building plans. If that same joist had gypsum ceiling l 240 the allowable deflection is 0 6. For example the allowable deflection of a 12ft span floor joist with plaster l 360 is 0 4 12ft divided by 360. See the table below.
Relatively longer spans and higher loads have the potential to make differential deflection problems in floors more pronounced. For floor joists a live load deflection limit of l 360 and a total load deflection limit of l 240 must be met. The 2012 international building code ibc section 1604 3 requires floor members supporting dead and live loads to not exceed an l 240 deflection limit. Codes don t regulate floor vibration.
A building s framing works in conjunction with its foundation to provide strength and. Got bounce appeared in the august 2012 issue of prosales and dealt with mitigating floor deflection in new home construction.